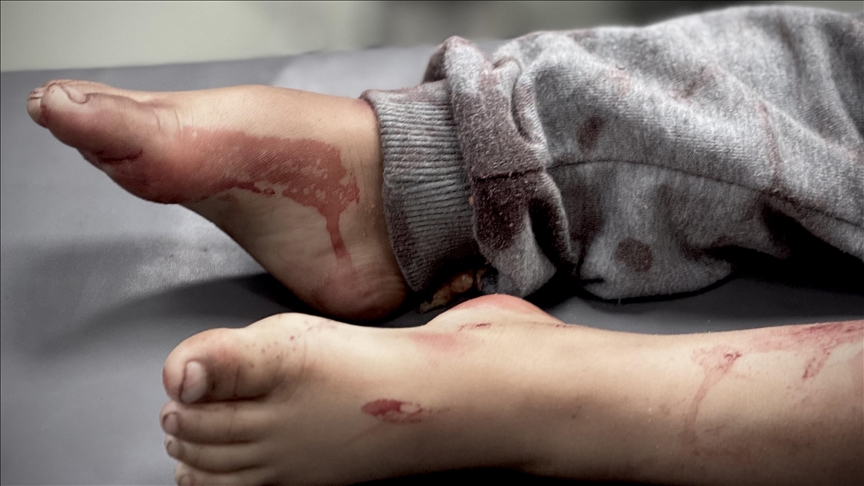
Israel Kills Children as World Looks on
Mark these words: South Africa is likely to win the genocide case at the International Court of Justice (ICJ), but by then, it will be too late to save a single civilian life. The time for robust action is now.
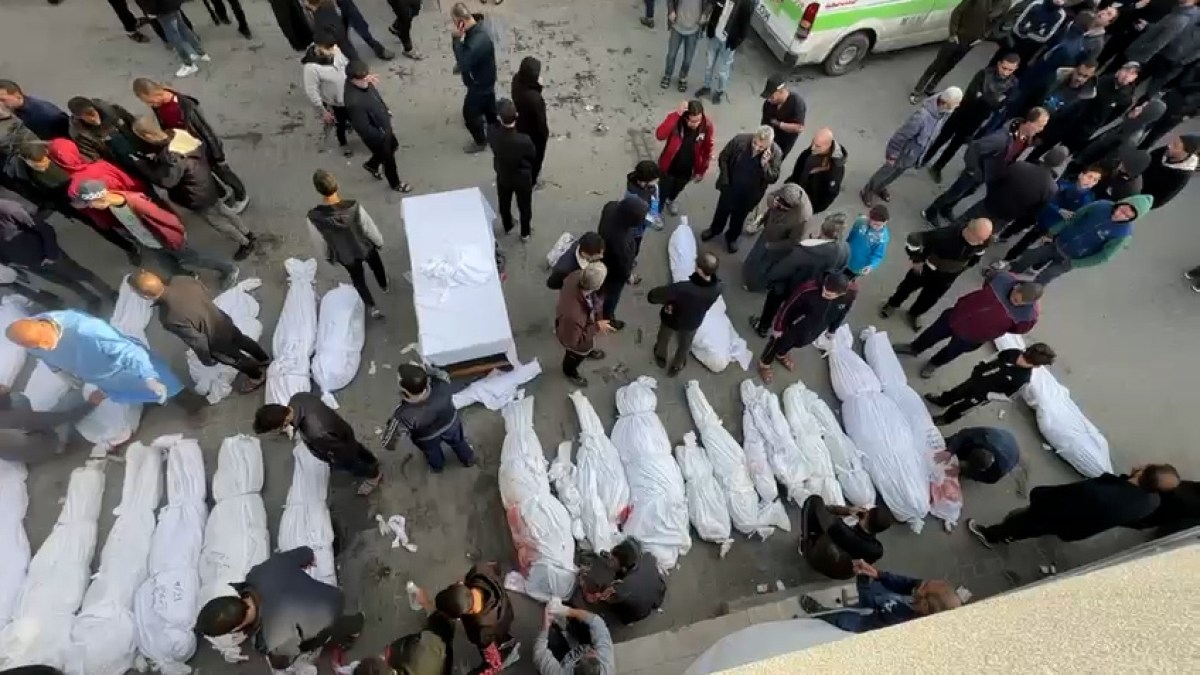
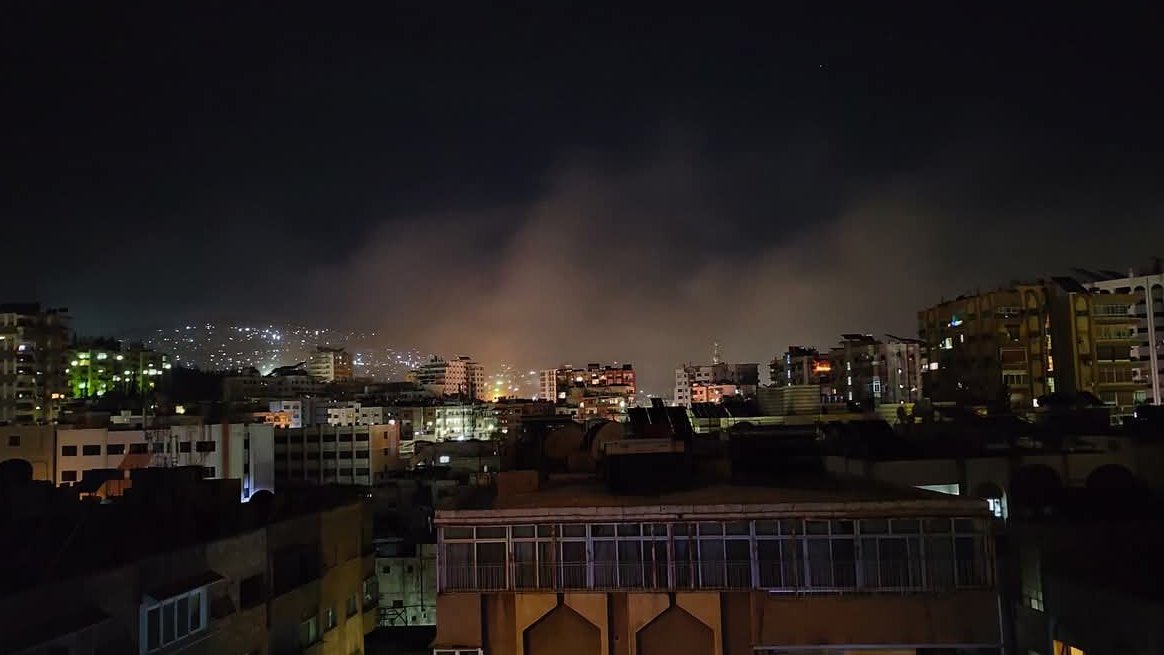
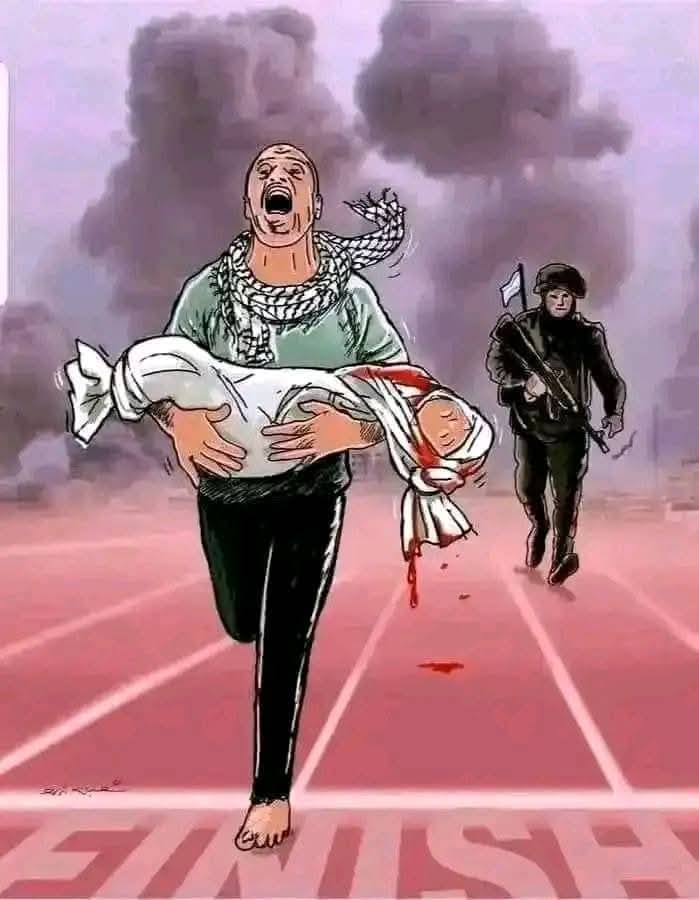
The resumption of the exterminatory Israeli bombardments on Gaza has killed 174 Palestinian children and toddlers in less than 48 hours, according to Defense for Children International. UNICEF has also denounced the killing of more than 130 children in a single day, representing the largest single-day child death toll among Palestinians in years. This may be the deadliest episode in the history of Israeli military actions in Palestine.
Family members of slain Israeli captives, whose names and faces have repeatedly been used to justify further attacks on Palestinians, condemned their government’s actions as another betrayal of the hostages, with Yarden Bibas writing “military pressure endangers the hostages while an agreement brings them home”, and networks of Israeli families declaring Israeli Premier Benjamin Netanyahu chose Ben-Gvir’s return to the government over the return of the hostages from Gaza.
In the midst of this carnage, Israeli ministers declare “a society that tolerates Hamas sympathizers within it has no right to exist,” or ask the very population they are destroying to “return the hostages and remove Hamas” unless they want to pay a “far more severe price” of “total devastation.”
Ideology of destruction
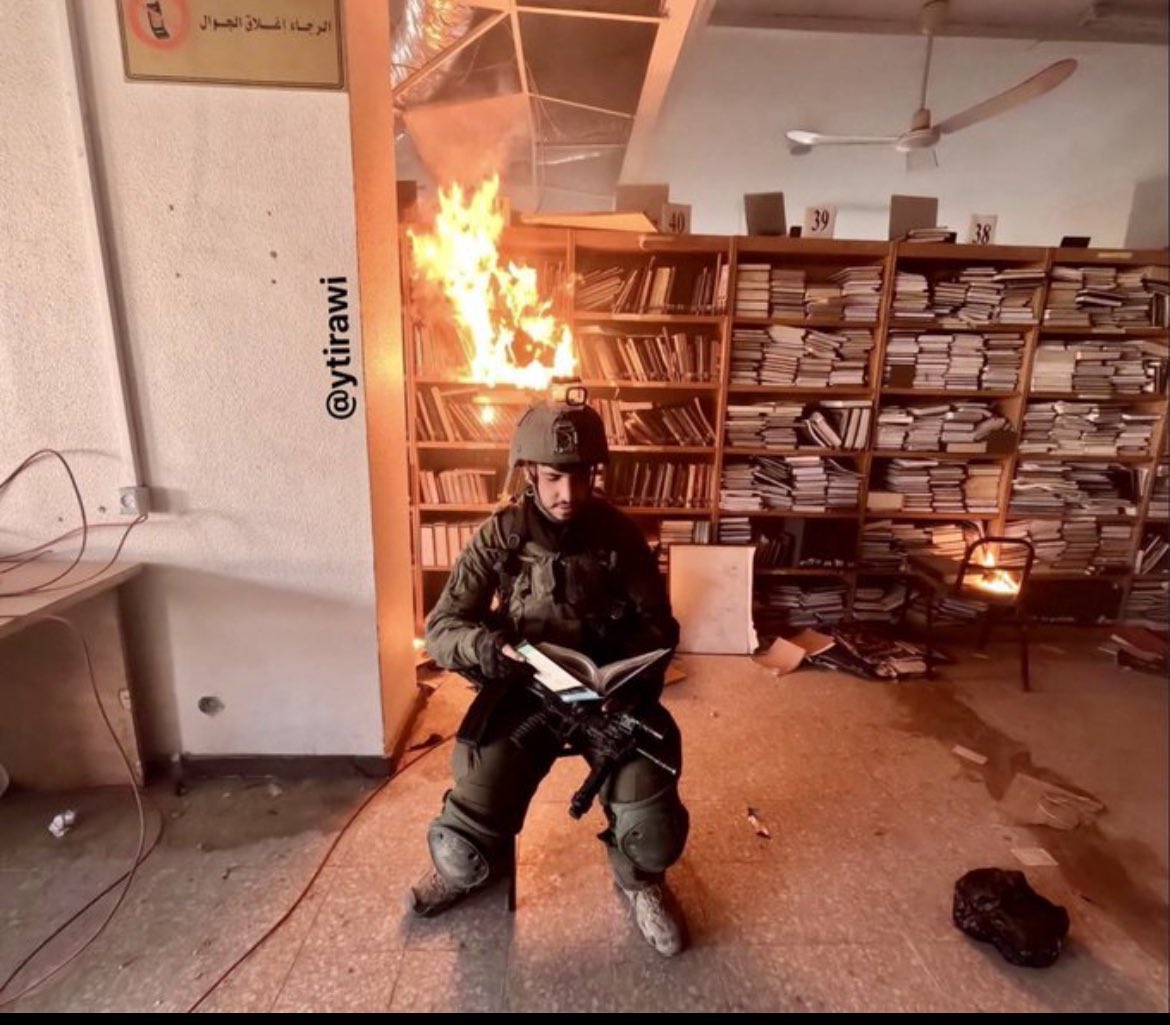
The ideology of the Israeli leadership is becoming increasingly explicit: It promotes the notion that Palestinians deserve elimination and are responsible for their own destruction. It is a paradigmatically genocidal ideology, typical of all the genocides in history, construing the victim group’s existence as undeserved, its survival as an intolerable threat, brutalities against it inherently justified, ‘called for’, and the forcing of the group into inexistence as a way of restoring the natural order of things as they should have always been. After all, key Israeli ministers declared “there is no such thing as a Palestinian people.” Declaring the inexistence of a people equates precisely to posing the premises for its elimination.
The honesty of the genocidal narratives of the Israeli executive, coupled with the use of hunger, thirst, diseases as weapons of war, reinforces crucially the validity of South Africa’s arguments at the ICJ, and of those states intervening in support of those arguments. As an international lawyer, my guess is that South Africa, even more likely after these renewed atrocities, will win the genocide case at the ICJ.
Despite the all-time record of crimes against children, Western states keep refraining from legal action, even those intervening in other ICJ cases to affirm that, in their interpretation of the Genocide Convention, the victimization of children, as the most vulnerable and crucial component of victim groups, should bring special weight in ascertaining the existence of genocidal intent. Beyond hypocrisy and racist double standards, Palestinian children are portrayed as less human and less worthy of protection than other children.
The irresponsibility of political leaders of third states indeed continues to kill. Silent when not complicit, incapable of acting for a single sanction, some are even offering safe harbors from ICC arrest warrants to their political and business partners wanted for war crimes and crimes against humanity, violating their own obligations as state parties of the Rome Statute.
In sum, the lawlessness unleashed on Palestinians is indeed infecting the world (dis)order, and it is evident that Netanyahu has all the interest in descending the entire region into a state of permanent war to stay in power. The global instability deriving from the winds of regional and global wars (in which the EU is diving rather than shifting its disastrous strategic approaches) will inevitably increase authoritarian repressions against dissidents, oppositions, and alternative visions in many of the countries revolving around this tragic abyss of history. War and authoritarianism always nurture each other. It is therefore not only in the interests of the survival of Palestinians, but a political necessity against the oligarchic shifts in our own countries to demand robust action now.
Protecting lives
Palestinians need a humanitarian intervention of a multilateral coalition to protect civilian lives. This presence alone can tackle an alliance of savage powers devaluing the lives of Palestinians as less than human and extracting profits from their massacres now, while preparing to extract more profits from exterminatory wars globally tomorrow. This would offer an immediate opportunity for world powers genuinely committed to reforming the international order towards a new multilateralism based on sovereign equality, self-determination, and peaceful coexistence to prove that their words are not empty slogans.
In other words, the paradox we face is that even the selfish pursuit of national interests—let alone legal or moral obligations—should be enough to trigger decisive action like the one proposed in this reflection.
A multilateral military presence, under UN auspices, to protect Palestinian civilians appears necessary as never before, since none of them will ever be safe under occupation by forces making clear they consider their existence as a people an offense to be redressed by annihilation. Should a coalition of states promote such an action, it would enjoy the support of masses of citizens across the globe, and gain moral leadership in these dark times, marked by the unchecked rise of international criminality.
Luigi Daniele is a senior scholar at Nottingham Trent University